UNHCR Online Application Form for Refugees and Asylum Seekers
The life of refugees in South Africa is becoming very difficult day by day. Since the start of covid-19, UNHCR has decided to join the South African government in order to collaborate with SASSA and ensure that all refugees with Asylum Seekers and Special Permit Holders benefit also from the SRD R350 Grant of which the payment will take place every after 6 months. So if you haven’t applied yet, you need to click here to Apply.
Due to what happened yesterday, 27 August 2024, more than 200 refugees were arrested by the police in the Durban CBD, therefore UNHCR officially opening an application form to all refugees and asylum seekers who are living in South Africa
Refugees and Asylum Seekers Interview
We would like to inform all refugees and asylum seekers that after submitting their application, we will contact them through their application cell phone numbers for their first interview.
We will put a list below of the questions that we will ask you during the interview, so we strongly advise you to be ready and write down the answers to those tricky questions for the first interview, because we will ask you the same question for the second interview.
If your interview goes well, we will invite you to come and collect your Refugee Identity Card at our office while waiting for our last next step which is your body health check up and give 500 US dollars for your purchases/ or shopping.
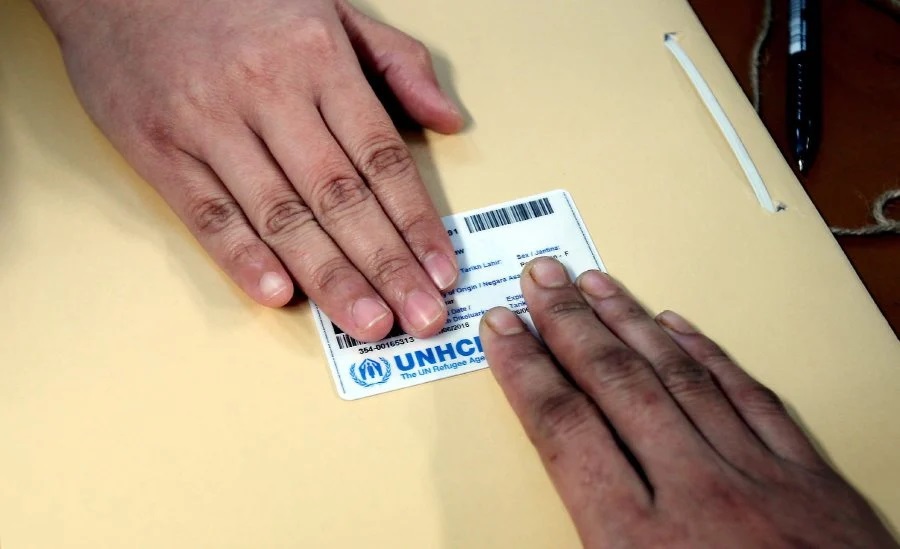


Like we said, the Refugees and Asylum seekers substantive interview is a chance for us to be sure if you are not lying and if your story checks out and Don’t worry if you feel overwhelmed. We will ask you some of our tricky questions which will be:
- About you
- Names
- Date of Birth
- Nationality
- Home Language
- Criminal records etc…
- About your asylum application
- Who is making you feel unsafe?
- What’s the treat you’re escaping?
- How did you collect your evidence?
- About your story
- Where were you born
- Last School Attended
- Biography of your Parents
- When did you arrived here?
- Why did you leave your country?
- What are you doing for a living here?
- When did you leave your home country?
- Do you have any family left there? Are you still in contact with them?
- Have you been to other countries? Have you tried to claim for asylum there?
- How many countries have you crossed to get here? and which transport did you use?
Try to answer each question as accurately as possible, without guessing or speculating.
For example, “When did you leave your home country?” If you remember the exact date, great! But often you might not remember specific dates – especially if you are not keeping a note of it.
What do you do in case you don’t know the date? Try to be as close to the actual date – which month? What season was it? Last summer? Was it around some festival that you remember?
Be prepared for the same questions to be asked again and again – don’t get rattled. Just keep a cool head, ask for water if you need it, take a break if it feels too overwhelming and start again, we will wait for you by putting a call on hold for 5 minutes.
REMEMBER: Even the simplest of questions might seem overwhelming when asked repeatedly. Be prepared to be pushed just a bit and don’t lose the number you applied with.
ACTION: Try to conduct at least one to two practice interviews with your lawyer/ or social worker to build your confidence, if possible.
NEXT: We will inform you of the latest decision regarding your application.
And don’t forget: You are valuable. You are powerful. You can do this!
Good Luck.
UNHCR Latest update

UNHCR Refugee Journey Overview
1. Country of Departure:
Refugees under the UNHCR program come from various countries experiencing conflict, persecution, or other humanitarian crises. Common departure countries include Syria, Afghanistan, South Sudan, DRC, Venezuela, and Myanmar, Burundi, among others. The departure process usually involves registration with the UNHCR in refugee camps or urban settings in neighboring countries where refugees initially seek asylum.
2. Destination Countries in Europe:
Refugees are resettled in various European countries based on resettlement agreements and quotas. Some of the primary destination countries in Europe include:
- Ireland
- Poland
- Sweden
- Norway
- Denmark
- Netherlands
3. Departure Process and Journey:
The resettlement process involves multiple steps:
- Registration and Assessment: Refugees are registered by the UNHCR and assessed based on vulnerability and protection needs.
- Interviews and Background Checks: Refugees undergo detailed interviews and background checks by resettlement countries to ensure eligibility and security.
- Travel Arrangements: Once accepted, refugees receive travel documents, medical screenings, and pre-departure orientation. The UNHCR and IOM (International Organization for Migration) facilitate their flights and other travel arrangements.
- Arrival and Reception: Upon arrival in Europe, refugees are received by local authorities, NGOs, and support organizations that help with integration.
4. Refugee Salary in Europe:
- General Overview: Upon arrival, refugees usually do not receive immediate employment but are provided with basic support, such as housing, healthcare, and financial aid, while they adjust and start the integration process.
- Employment and Salary:
- Refugees are allowed to work once their status is confirmed and they receive the necessary permits.
- Average Salary per Hour: The hourly wage varies significantly across Europe depending on the country, local labor market, and job type. However, as a rough guide:
- Ireland: €12-15 per hour for entry-level jobs.
- Poland: Around €12-14 per hour
- Sweden: €11-14 per hour.
- Norway: €10-12 per hour (minimum wage is around €11 per hour).
- Denmark: €10-12 per hour.
- Netherlands: €11-13 per hour.
- Factors Affecting Salary: Refugee salaries depend on language skills, education level, professional experience, and the local job market conditions.
5. Integration Challenges and Support:
- Language Barriers: Language proficiency is often a significant hurdle for refugees in finding well-paying jobs.
- Skill Recognition: Many refugees struggle with getting their qualifications recognized, limiting job opportunities.
- Support Services: European countries offer various integration programs, including language courses, job training, and counseling services to help refugees integrate into society and the workforce.
UNHCR Refugees and Asylum seekers Process
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) does not directly transport people to Europe. Instead, UNHCR focuses on protecting and assisting refugees and asylum-seekers, including facilitating resettlement and providing humanitarian aid in various regions. Here’s a detailed overview of how the process works and how UNHCR supports refugees, leading some to find pathways to Europe:
1. Identification and Registration:
- Initial Contact: Refugees often arrive in countries neighboring conflict zones or areas of persecution. UNHCR identifies and registers individuals in need of protection.
- Documentation: Refugees are issued documents confirming their status, which is crucial for access to aid, legal protection, and potential resettlement opportunities.
2. Refugee Camps and Support Centers:
- Temporary Shelters: Many refugees live in camps or urban areas supported by UNHCR, receiving food, medical care, education, and other basic services.
- Protection Services: UNHCR provides legal assistance and protection against forced return (refoulement), while working to ensure refugees’ safety and dignity.
3. Resettlement Programs:
- Resettlement Selection: Only a small fraction of refugees is eligible for resettlement. UNHCR identifies the most vulnerable individuals, such as survivors of violence, families with urgent medical needs, or those facing severe threats in their current location.
- Country Quotas: UNHCR works with countries that accept refugees for resettlement, including several European nations. Each country sets quotas and criteria for accepting refugees.
- Application Process: UNHCR helps refugees apply for resettlement, preparing dossiers and coordinating interviews with officials from potential host countries.
4. Preparing for Resettlement:
- Cultural Orientation: Refugees often receive cultural orientation sessions to help them understand what to expect in the new country, covering language, culture, laws, and rights.
- Medical Checks and Travel Documents: Medical examinations ensure refugees are fit to travel, and necessary documents (e.g., visas) are obtained.
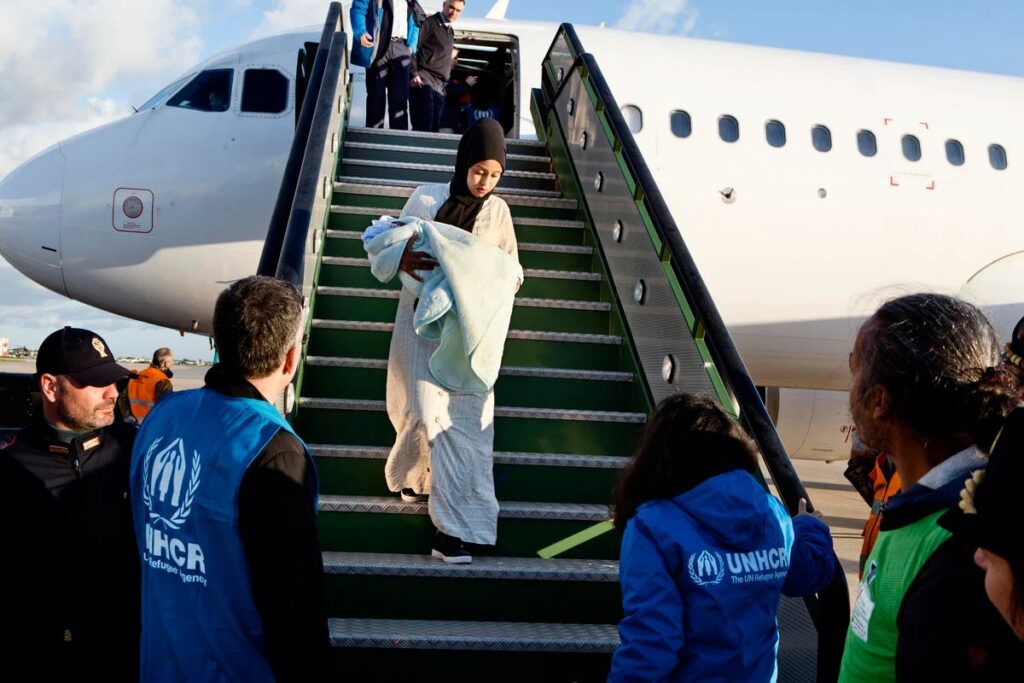
5. Transportation to Europe:
- Logistics Coordination: While UNHCR doesn’t provide transportation directly, it coordinates with the International Organization for Migration (IOM) to facilitate travel arrangements for resettled refugees.
- Safe Passage: Refugees are usually flown to Europe, where they are received by local authorities and NGOs.
6. Integration in the Host Country:
- Arrival Support: Upon arrival, refugees are greeted and supported through the initial stages of settlement. They receive temporary housing, access to social services, and language classes.
- Long-term Integration: Host countries assist refugees with long-term integration, including finding permanent housing, employment opportunities, and access to education and healthcare.
7. Other Legal Pathways:
- Family Reunification: Some refugees reach Europe through family reunification programs, which allow immediate family members of those already granted asylum to join them legally.
- Humanitarian Visas: Certain European countries issue humanitarian visas, allowing refugees to travel legally for the purpose of seeking asylum.
Challenges and Misconceptions:
- Misconception of Mass Transport: There’s a common misconception that UNHCR directly transports large numbers of refugees to Europe. In reality, only a tiny percentage of the global refugee population is resettled.
- Smugglers vs. Legal Routes: Many refugees’ resort to dangerous routes and smugglers to reach Europe, risking their lives. UNHCR continuously advocates for safer, legal pathways.
How does refugees receive support from UNHCR
The process of how refugees receive assistance, including financial support and documentation in Europe, involves multiple steps, organizations, and procedures. Here’s an overview of how the UNHCR (United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees) and other relevant bodies are involved:
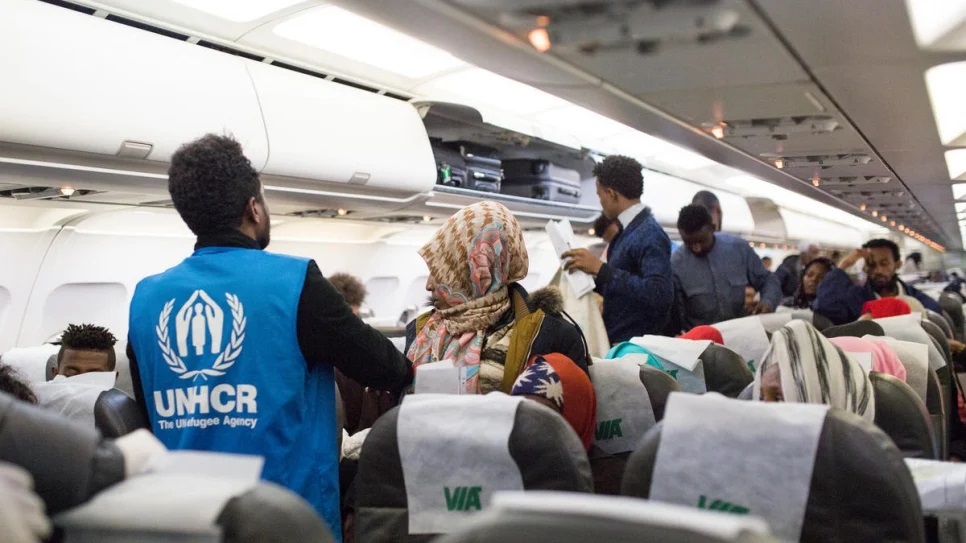
1. Reaching Europe:
- Routes: Refugees typically reach Europe via land, sea, or air. Common routes include crossing the Mediterranean Sea, overland through Turkey and the Balkans, or through legal humanitarian corridors.
- Smugglers and Risks: Many use smugglers, facing risks like dangerous journeys, exploitation, and harsh conditions.
2. Reception Upon Arrival:
- Initial Contact: Upon arrival, refugees are usually met by local authorities, coast guards, or NGOs. They are taken to reception centers or camps where they receive immediate aid.
- Screening: Authorities conduct security screenings, health checks, and register asylum seekers. This process is usually handled by national immigration services, sometimes in cooperation with the UNHCR.
3. Financial Support:
- Cash Assistance: UNHCR and local governments provide financial aid to help refugees meet their basic needs. This is often done via prepaid cards, direct cash distributions, or bank transfers.
- Criteria for Assistance: The amount and duration of financial support depend on the refugee’s vulnerability, legal status, and country of asylum. Factors include family size, age, health status, and access to other aid.
4. Reception and Housing:
- Reception Centers: Refugees are often first placed in reception centers, which provide basic shelter, food, and medical care.
- Integration Programs: After initial reception, they may be moved to more permanent housing, often arranged by local municipalities, NGOs, or volunteer organizations.
5. Document Issuance:
- Registration and Asylum Application: Refugees need to apply for asylum to obtain legal status. During this process, they receive temporary documents that grant them rights to stay in the country until a decision is made.
- Residence Permits: Once granted asylum, refugees receive residence permits that allow them to work, study, and access public services.
6. Credit and Financial Access:
- Opening Bank Accounts: Refugees can open bank accounts with the help of residence permits and other identification provided during the asylum process. Financial literacy programs also help them manage their finances.
- Social Security and Benefits: They may also access social benefits like healthcare, education, and sometimes unemployment benefits, depending on the host country’s policies.
7. Who Receives Them:
- Authorities and NGOs: Local authorities, the UNHCR, IOM (International Organization for Migration), and numerous NGOs are involved in receiving, processing, and supporting refugees.
- Community and Volunteer Organizations: Many grassroots organizations and volunteers also provide support, helping refugees integrate into local communities.
8. Taking Credit:
- Government and UN Agencies: Host governments, international bodies like the UNHCR, and the European Union often highlight their efforts in supporting refugees, especially in public reports and media.
- NGOs and Civil Society: NGOs, both large and small, often publicize their work to attract donations and public support, highlighting their role in aiding refugees









Comments
One response to “UNHCR Hasani Online Application Form for Refugees and Asylum Seekers”